Science—神经科学的“密码系统”被发现:科学家发现决定特定神经元类型的转录密码
时间:2022-12-15 21:01:09 热度:37.1℃ 作者:网络
中文摘要
神经系统中细胞类型的多样性对解析其编码遗传机制提出了挑战。在这项研究中,科学家报道了果蝇视觉系统中近200个不同的神经元都可以由约10个连续表达的转录因子的独特组合来定义。他们发现,上述转录密码的靶向修饰可诱导神经元命运的可预测转换,而且这种转换在形态学上和转录水平上都是完整的。对开放染色质的顺式调控分析可将这些基因与上游模式因子联系起来,而上游模式因子可定义干细胞向不同神经元类型分化的命运。经实验验证的网络模型描述了在大脑连接发育过程中,终端密码器和蜕皮激素信号对下游效应器的协同调节。他们的结果为有丝分裂后神经元如何实现特定的命运提供了一个可统一的框架。
英文摘要
The large diversity of cell types in nervous systems presents a challenge in identifying the genetic mechanisms that encode it. Here, we report that nearly 200 distinct neurons in the Drosophila visual system can each be defined by unique combinations of ~10 continuously expressed transcription factors. We show that targeted modifications of this terminal selector code induce predictable conversions of neuronal fates that appear morphologically and transcriptionally complete. Cis-regulatory analysis of open chromatin links one of these genes to an upstream patterning factor that specifies neuronal fates in stem cells. Experimentally validated network models describe the synergistic regulation of downstream effectors by terminal selectors and ecdysone signaling during brain wiring. Our results provide a generalizable framework of how specific fates are implemented in postmitotic neurons.

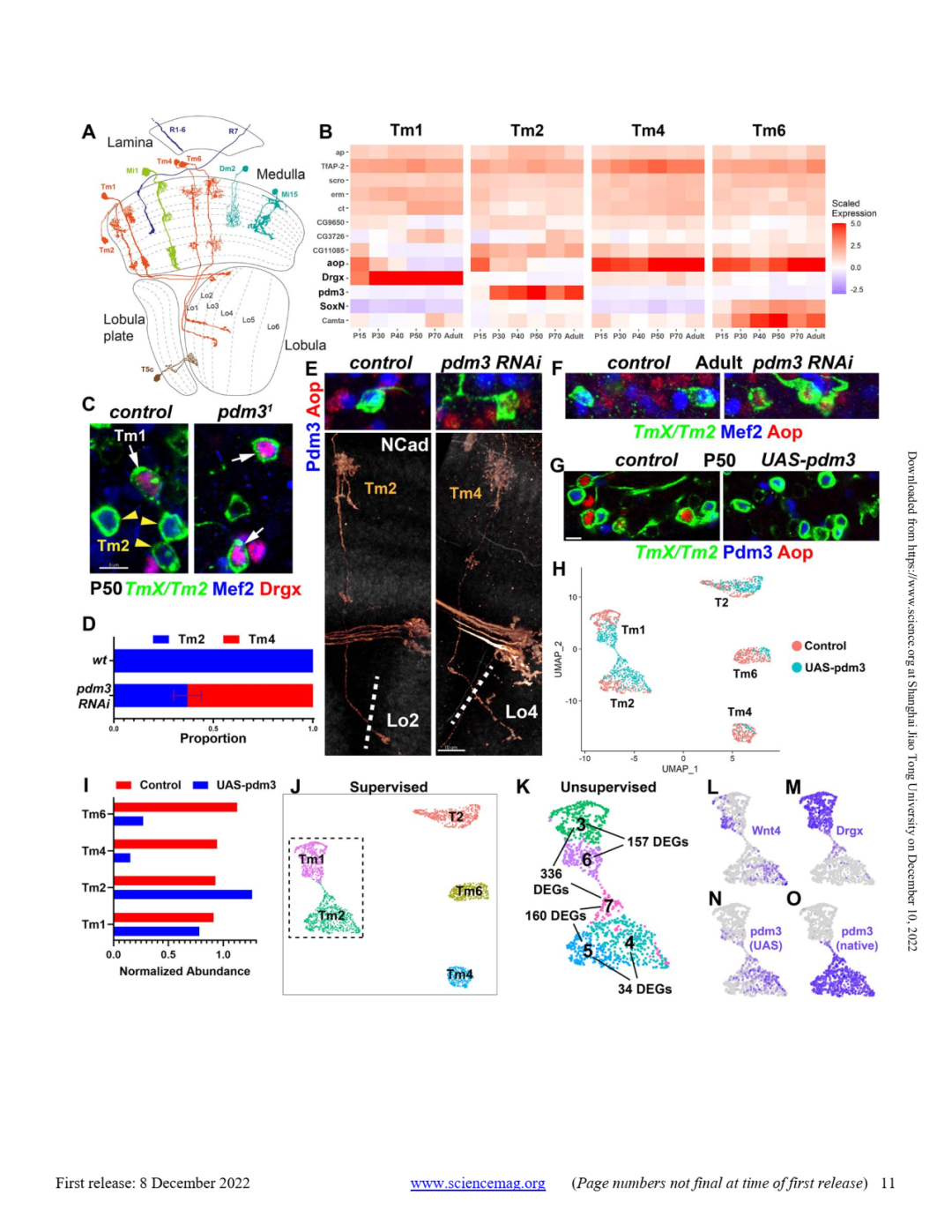
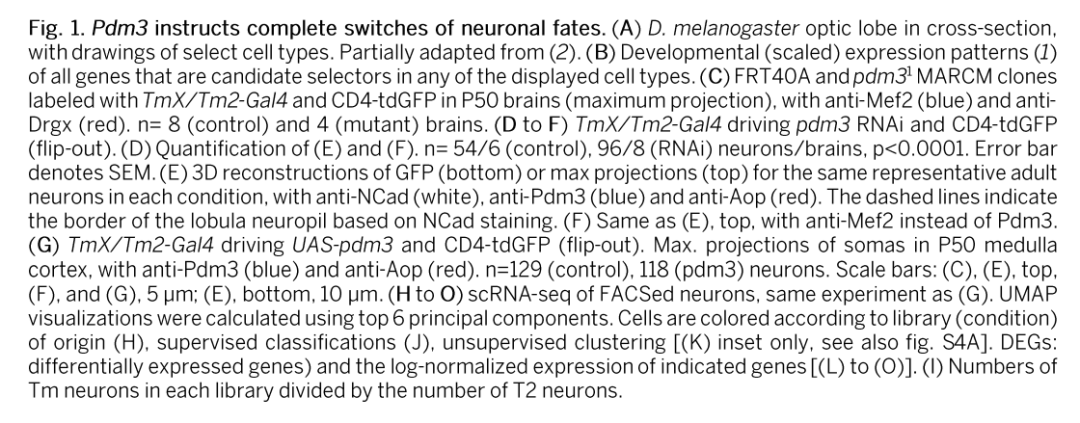
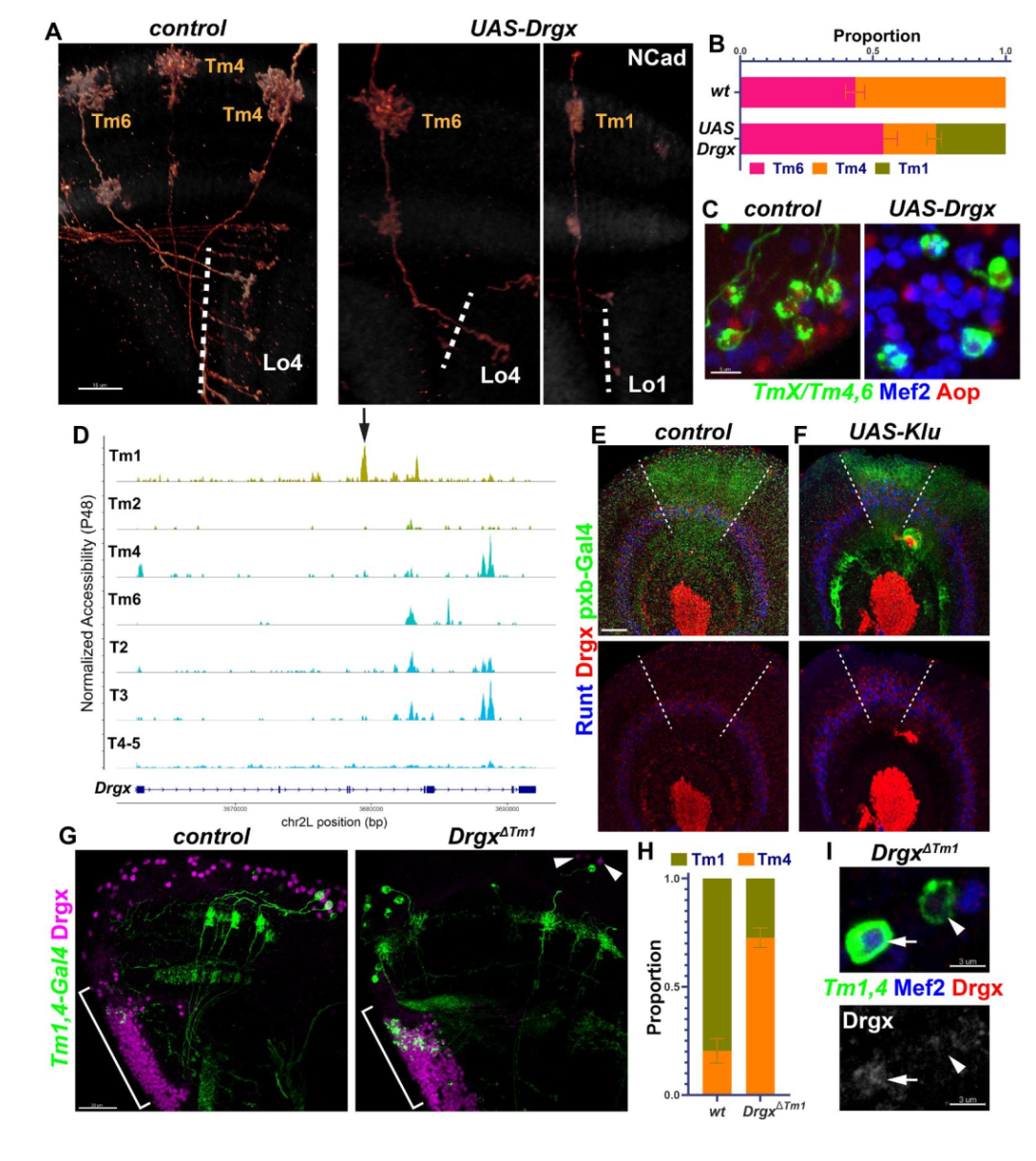


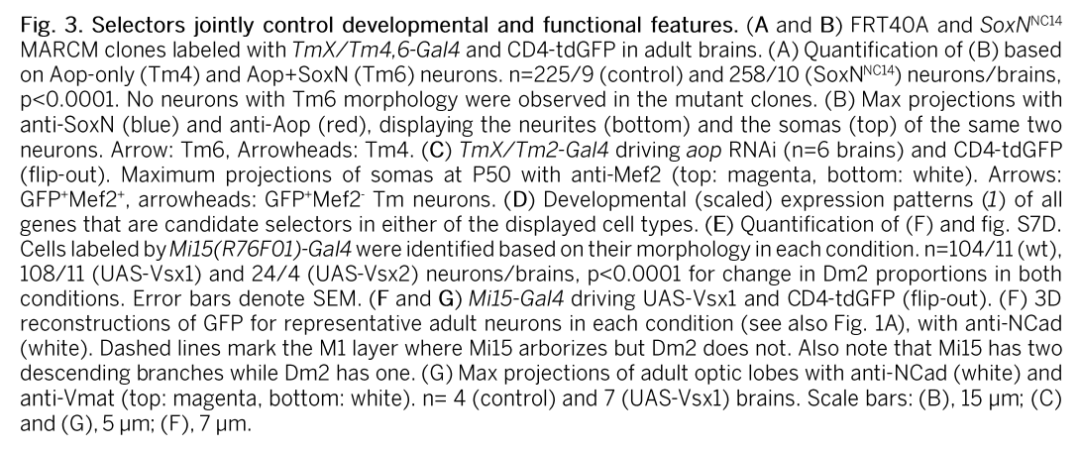

参考文献:Coordinated control of neuronal differentiation and wiring by sustained transcription factors. Science. 2022 Dec 8;eadd1884. doi: 10.1126/science.add1884. Online ahead of print.
: , 。 视频 小程序 赞 ,轻点两下取消赞 在看 ,轻点两下取消在看


